India's energy landscape is transforming rapidly, with the country on a mission to increase the share of renewable energy in its overall energy mix. A crucial component driving this transition is the Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO). RPO mandates that specific entities, primarily electricity distribution companies, purchase a minimum percentage of their power from renewable sources. This article will explore how RPO is fostering the growth of renewable energy in India, supporting policy goals, stimulating green investments, and shaping a sustainable future.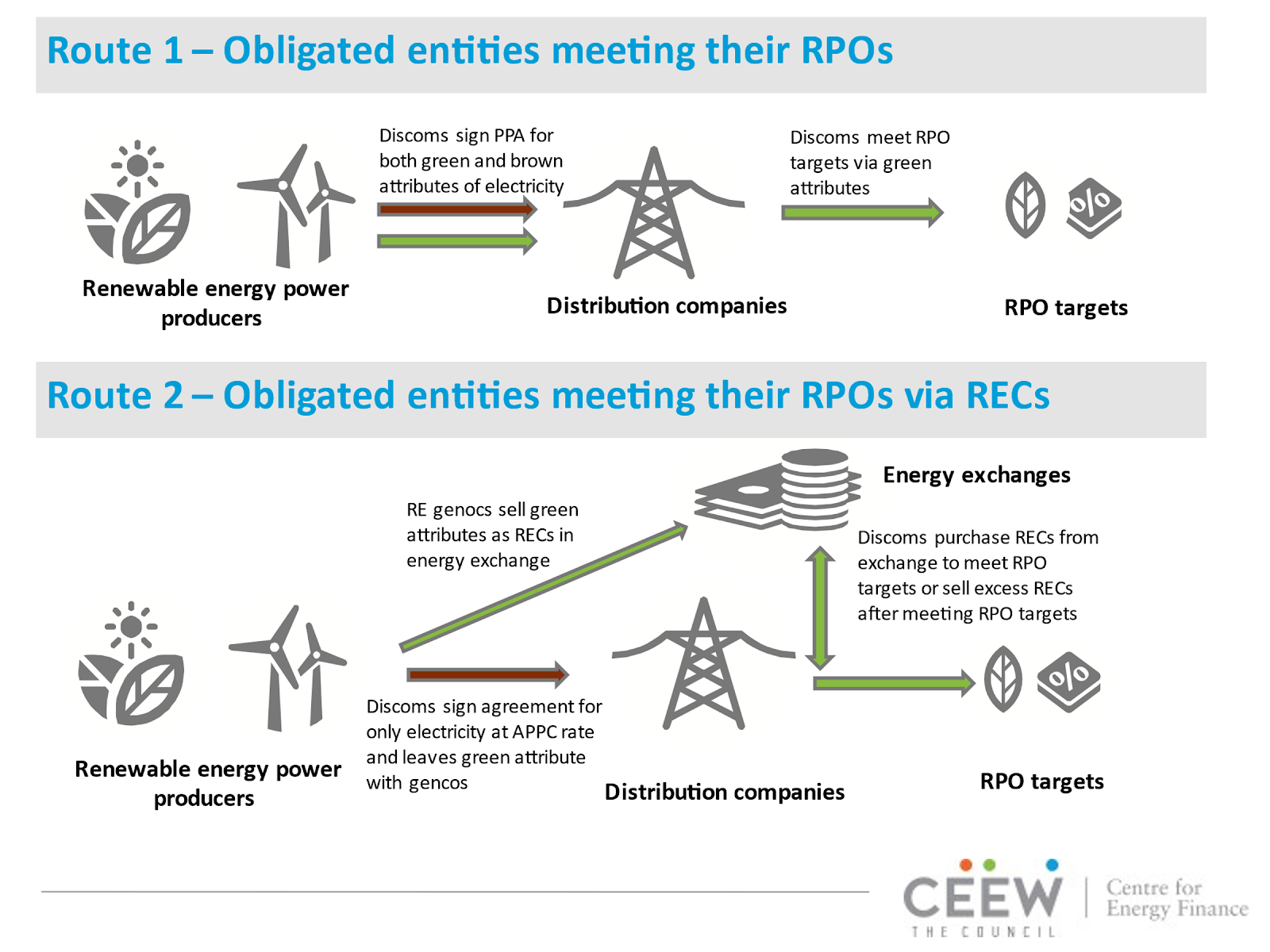
What is Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO) in India?
The Renewable Purchase Obligation is a regulatory framework introduced by the Government of India to promote the adoption of renewable energy. Under the Electricity Act of 2003 and the National Tariff Policy of 2006, it became mandatory for specific entities, especially electricity distribution companies (Discoms), open access consumers, and captive power plants, to meet a part of their energy requirements through renewable sources.
RPOs are categorized into two segments:
- Solar RPO: This requires obligated entities to purchase a specified percentage of electricity from solar sources.
- Non-Solar RPO: This covers other renewable sources like wind, biomass, and small hydropower.
Over the years, RPO targets have been increased gradually to meet India's evolving clean energy goals. These targets are updated periodically by state and central authorities and are instrumental in setting a clear path for renewable energy growth.
The Strategic Importance of RPO in India's Energy Goals
India has set ambitious targets for renewable energy deployment, aiming for 500 GW of installed capacity by 2030. RPO is one of the primary mechanisms to achieve this goal. By mandating renewable energy procurement, RPO helps:
-
Increase Renewable Capacity: RPO mandates create steady demand for renewable energy, encouraging both private and public sector investments in renewable projects, particularly solar and wind energy.
-
Attract Investments: RPO targets provide certainty for investors, allowing them to participate in a stable market where demand for renewable energy is consistently growing.
-
Facilitate Compliance with Climate Goals: By ensuring that a portion of the energy mix comes from renewable sources, RPO helps India meet its obligations under international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement.
-
Decentralize and Democratize Energy Production: RPO encourages renewable energy adoption across states, contributing to energy security and supporting smaller, distributed energy systems like rooftop solar and microgrids.
How RPO Drives Market Dynamics and Innovation?
The RPO framework has stimulated innovation in multiple aspects of India's renewable energy sector. Here's how:
Emergence of Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)
To ensure flexibility in meeting RPO targets, the government introduced the Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) mechanism in 2010. RECs allow obligated entities to fulfill their RPO requirements even if they are unable to directly procure renewable energy. By purchasing RECs, they can symbolically represent renewable energy consumption. This has created a secondary market for renewables, promoting financial innovation and helping meet RPO targets cost-effectively.
Development of Solar Parks and Hybrid Projects
To meet the increasing demand for renewable energy under RPO, the government has supported the development of large-scale solar parks, wind farms, and hybrid projects. Hybrid renewable energy projects, which combine solar and wind energy generation, are gaining traction. These projects offer more consistent power output, addressing intermittency challenges that often hinder renewable energy.
Boost to Rooftop Solar Market
RPO mandates have also driven interest in distributed energy resources like rooftop solar, particularly among commercial and industrial (C&I) consumers. C&I consumers who cannot directly source renewable energy can invest in rooftop solar and on-site generation to meet RPO targets, driving growth in this segment.
State-Level Initiatives and Innovation
India's diverse energy landscape allows individual states to set customized RPO targets based on their renewable resource potential. States like Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu have implemented more ambitious RPO targets than required, spurring regional innovations in clean energy technology and infrastructure.
Challenges in Implementing RPO
While RPO has been a driving force in India's renewable energy transition, it faces several challenges that need addressing for successful implementation:
-
Compliance Issues: Compliance with RPO targets has been inconsistent across states, largely due to the financial strain on Discoms. Some Discoms have delayed or defaulted on RPO targets, affecting overall progress.
-
Lack of Enforceability: Although RPO mandates are legally binding, enforcement mechanisms are sometimes weak. States and regulatory commissions must ensure strict compliance to meet national renewable targets.
-
Financial Viability of Discoms: Many Indian Discoms struggle with financial challenges that impede their ability to procure renewable energy or pay for RECs. Financial restructuring and government support are critical for making Discoms viable participants in India's renewable energy market.
-
Price Fluctuations in REC Market: While RECs provide flexibility, market fluctuations in REC prices can disrupt the balance of supply and demand. This affects the predictability and affordability of RPO compliance for obligated entities.
Recent Policy Developments Enhancing RPO
In response to challenges, the Indian government has introduced several reforms to enhance the effectiveness of RPO:
-
Green Term Ahead Market (GTAM): Launched by the Indian Energy Exchange, GTAM is a platform where obligated entities can trade green energy. GTAM enables the trading of renewable power on short-term contracts, providing more flexibility in meeting RPO requirements.
-
RPO Compliance Audits: The Ministry of Power has recommended stricter monitoring and audits of RPO compliance. This includes annual audits and financial penalties for non-compliance, which will help ensure states and Discoms meet their targets.
-
Higher RPO Targets Under Draft National Renewable Energy Policy: India's Draft National Renewable Energy Policy proposes higher RPO targets in line with the 500 GW renewable energy capacity goal for 2030. This will drive faster adoption and incentivize investment in a broader range of renewable technologies.
The Future of Renewable Energy in India through RPO
RPO is positioned to play a transformative role in India's renewable energy future. As compliance mechanisms strengthen and RPO targets increase, India will see significant growth in solar, wind, and hybrid projects, ultimately helping to decarbonize the power sector. Here are a few ways RPO is shaping the future of renewable energy in India:
-
Energy Transition Acceleration: The RPO trajectory aligns with India's long-term goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070. As RPO targets increase annually, India's energy transition will gather momentum, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
-
Grid Modernization and Energy Storage: Higher RPO targets will necessitate grid upgrades to manage increased renewable capacity. Investments in grid-scale battery storage, demand response, and energy management solutions will increase as RPO pushes India toward a more resilient, green grid.
-
New Opportunities in Renewable Energy Ecosystem: Increased RPO targets will drive investments in newer technologies like offshore wind, green hydrogen, and advanced solar technologies. These innovations will diversify India's renewable portfolio, ensuring a reliable and robust energy mix.
-
Employment and Economic Growth: The growing renewable sector, fueled by RPO, will create employment opportunities across sectors, from manufacturing solar panels and wind turbines to R&D and installation. This economic ripple effect will benefit local communities and contribute to India's economic growth.
Conclusion
The Renewable Purchase Obligation has emerged as a powerful tool in India's renewable energy journey, effectively shaping a sustainable future. By mandating renewable energy procurement, the RPO framework has provided a clear pathway for renewable capacity growth, supporting India's commitment to climate goals and green energy transition. Although challenges remain, recent policy improvements and stricter compliance mechanisms signal a positive shift.
India's commitment to increasing RPO targets, combined with continued innovations in renewable energy, holds great promise for achieving an energy-secure, low-carbon future. As India races towards its 2030 and 2070 climate milestones, RPO will remain central to its strategy, shaping a renewable future that powers economic growth and environmental resilience.





